Disclosure: This Post Contains Affiliate Links; We earn a commission on purchases.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can be a significant problem for sensitive electronic devices. EMI occurs when one source disrupts another source’s signal, leading to device failure and decreased performance. To protect against EMI, shielding materials are used to prevent electromagnetic interference. There are various materials available for EMI shielding, each with its own properties and effectiveness.
When comparing shielding materials, it’s crucial to consider factors like conductivity, corrosion resistance, and shielding effectiveness. By understanding the different options, you can choose the right material that suits your specific needs and provides optimal EMI protection for your electronic devices.
Key Takeaways:
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can disrupt the signals of sensitive electronic devices, causing device failure.
- EMI shielding materials are used to prevent interference and protect electronic devices from EMI.
- Materials like aluminum, copper, pre-tin plated steel, and copper alloy 770 have different properties and effectiveness in reducing interference.
- Consider factors like conductivity, corrosion resistance, and shielding effectiveness when choosing the right shielding material.
- Proper EMI shielding is crucial for protecting sensitive electronics and preventing interference-related issues.
What is Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)?
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a phenomenon that occurs when one source disrupts another source’s signal, leading to potential device failure. EMI can impact electrical circuits through induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction.
There are two main types of EMI: narrow-band and broadband. Narrow-band EMI typically occurs with devices such as radios, TV stations, and mobile phones. This type of interference can often be tuned out without causing significant damage.
On the other hand, broadband EMI occurs over a broader spectrum and can pose more severe threats to devices, especially those equipped with digital data links. The wide range of frequencies involved makes it challenging to mitigate and can result in more serious consequences if left unaddressed.
Where Does EMI Come From?
EMI, or electromagnetic interference, can originate from both man-made and natural sources. Understanding the various sources of EMI is crucial in order to effectively protect electronic devices from its negative effects.
Man-Made Sources of EMI
Man-made sources of EMI include:
- Ignition systems
- Power lines
- Devices that emit energy over radio frequencies
These sources can generate electromagnetic fields that interfere with the functioning of nearby electronic devices.
Natural Sources of EMI
Natural sources of EMI include:
- Solar flares
- Lightning
These natural phenomena can produce powerful electromagnetic disturbances that can impact electronic equipment.
In addition to man-made and natural sources, interference can also be caused by large equipment, basic communication devices, and older devices without proper shielding.

The Impact of EMI
EMI can have significant negative effects on electronic devices, including:
- Hardware damage
- Data loss
- Decreased productivity
It is essential to identify and address the sources of EMI to ensure the reliable operation of electronic devices and prevent potential damage or data loss.
What is EMI Shielding and How Does It Work?
EMI shielding, also known as electromagnetic shielding, is the use of specialized materials to prevent electromagnetic interference. It is a critical process in protecting the sensitive electronics of devices and preventing the absorption of unwanted signals. EMI shielding shields electronic equipment from both radiated and conducted electromagnetic emissions, reducing the risk of interference that can disrupt the proper functioning of devices.
EMI shields are typically constructed using metallic screens or enclosures that surround the sensitive electronics. These shields absorb and redirect electromagnetic waves, preventing them from reaching the internal circuitry of the device. By providing a physical barrier, EMI shielding materials create a shielded environment that protects against electromagnetic interference.
One essential aspect of EMI shielding is establishing a proper ground connection or virtual ground plane. This connection helps absorb and dissipate the unwanted electromagnetic energy safely, preventing it from affecting sensitive circuits and components. Grounding is crucial for maintaining the overall effectiveness of the EMI shield.
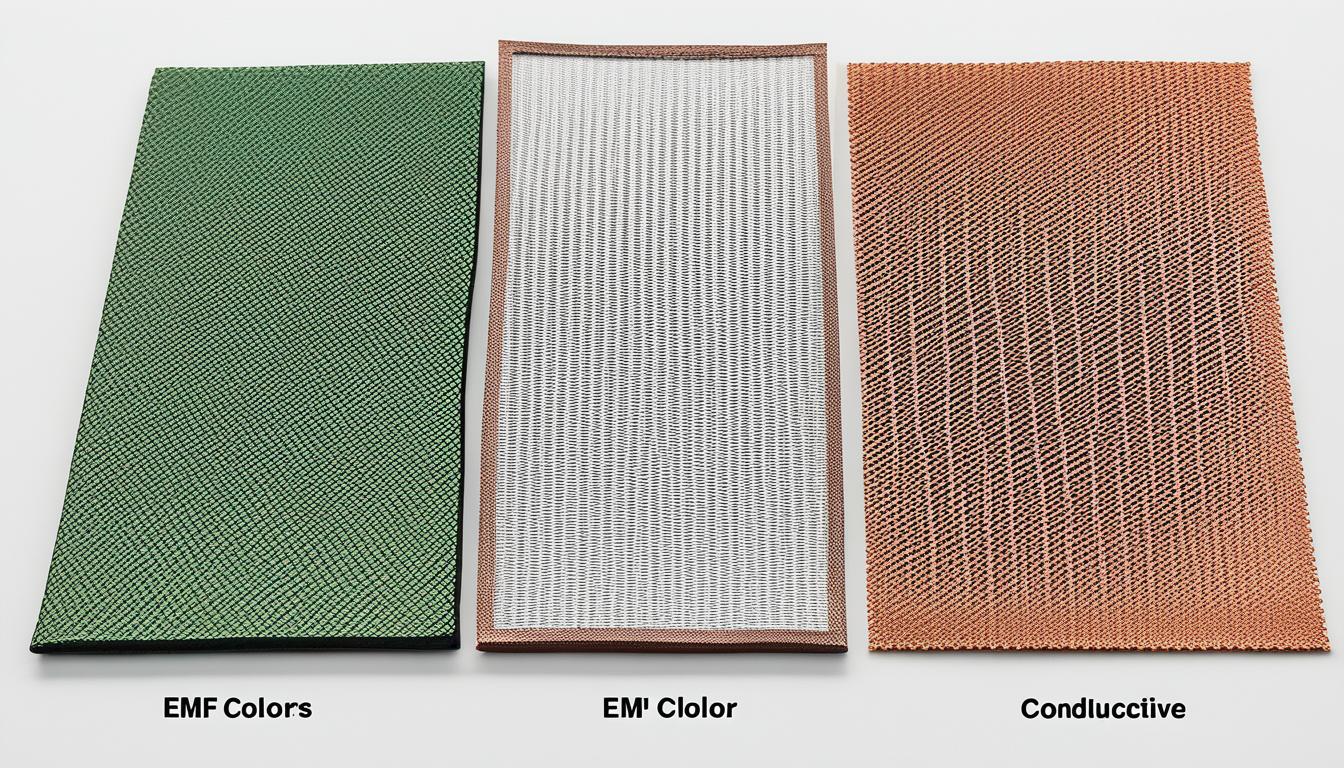
There are several materials commonly utilized for EMI shielding. These materials possess different properties and effectiveness in reducing interference. Some of the commonly used shielding materials include:
- Pre-tin plated steel: This material provides excellent magnetic shielding and is commonly used in electronic enclosures.
- Copper alloy 770: A highly conductive material that offers exceptional shielding effectiveness.
- Copper: Known for its high electrical conductivity, copper is widely used in EMI shielding applications.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and cost-effective, aluminum is commonly used in shielding applications where weight is a concern.
It is essential to choose the appropriate shielding material based on the specific requirements of the electronic device and the frequency range of the electromagnetic interference. Conductivity, corrosion resistance, and shielding effectiveness are crucial factors to consider when selecting the most suitable material for EMI shielding.
| EMI Shielding Material | Conductivity | Corrosion Resistance | Shielding Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-tin plated steel | High | Good | Excellent |
| Copper alloy 770 | High | Excellent | Exceptional |
| Copper | High | Good | Very Good |
| Aluminum | Medium | Good | Good |
The table above provides a comparison of the key characteristics of different EMI shielding materials. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision to ensure effective EMI protection for your electronic devices.
EMI Shielding Gaskets
EMI shielding gaskets play a crucial role in protecting electronics from interference. These gaskets are seals that fill the spaces between two surfaces, forming a barrier against electromagnetic interference (EMI). Made from particle-filled silicones, EMI shielding gaskets are specifically designed to provide durable and reliable protection.
These gaskets find extensive use in various industries, including the medical, data, and tech sectors. In the medical industry, EMI shielding gaskets are commonly employed on communication devices and patient monitoring equipment, ensuring the integrity and reliability of crucial medical equipment. In the data and tech industries, these gaskets protect sensitive data stored on RFID chips and other devices from EMI-induced corruption or loss.
One of the key advantages of EMI shielding gaskets is their ease of fabrication and cost-effectiveness. They can be easily manufactured in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different electronic components and applications. This versatility makes them an ideal solution for shielding sensitive electronics from EMI.
“EMI shielding gaskets provide reliable protection against electromagnetic interference, ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of electronic devices.”
By using EMI shielding gaskets, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and performance of their electronic devices. The ruggedized nature of these gaskets ensures long-lasting durability, making them ideal for applications that require continuous protection against EMI.
To showcase the effectiveness of EMI shielding gaskets, let’s take a look at a comparison table:
| Gasket Material | Conductivity | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle-Filled Silicones | High | Excellent | Cost-effective |
| Foam-In-Place Gaskets | Good | Good | Moderate |
| Elastomer Gaskets | High | Good | High |
As shown in the table, particle-filled silicones, the primary material used in EMI shielding gaskets, offer high conductivity, excellent durability, and cost-effectiveness. These properties make them an optimal choice for EMI protection in various industries.
Overall, EMI shielding gaskets provide a reliable and efficient solution for protecting electronics from electromagnetic interference. They are easy to fabricate, cost-effective, and ruggedized for durability. Whether in the medical, data, or tech sectors, utilizing EMI shielding gaskets ensures the integrity and performance of electronic devices, safeguarding against the harmful effects of EMI.
Conclusion
When it comes to protecting your electronic devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI), choosing the right shielding material is crucial. Factors such as conductivity, corrosion resistance, and shielding effectiveness should be taken into account.
There are several materials available for EMI shielding, each with its own unique properties. Aluminum, copper, pre-tin plated steel, and copper alloy 770 are commonly used and offer different levels of protection against EMI.
The choice of shielding material ultimately depends on the specific needs of your electronic device and the frequencies it operates on. By selecting the best material for shielding, you can ensure effective EMI protection and safeguard your devices from potential failure or data loss.
In conclusion, EMI shielding is essential for protecting sensitive electronics and preventing interference. Consider the properties of different materials and choose the most suitable one for your needs. With the right shielding material, you can ensure the proper functioning and longevity of your electronic devices.
Source Links
- https://leadertechinc.com/the-three-most-popular-shielding-metals-and-what-you-should-know-about-them/
- https://www.strouse.com/blog/what-is-emi-shielding
- https://www.wieland-diversified.com/blog/the-best-metals-to-protect-against-emi/

Subscribe to Our Newsletter